Thyroid Ultrasound
For Appointments Call: 786-332-4106 Miami 954-893-3811 Broward
Ultrasound of the Thyroid
- What is Ultrasound of the Thyroid?
- What are some common uses of the procedure?
- How should I prepare?
- What does the equipment look like?
- How does the procedure work?
- How is the procedure performed?
- What will I experience during and after the procedure?
- Who interprets the results and how do I get them?
- What are the benefits vs. risks?
- What are the limitations of Ultrasound of the Thyroid?
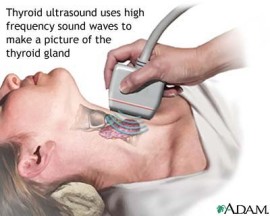
What is an Ultrasound of the Thyroid?
Ultrasound imaging, also called ultrasound scanning or sonography, involves the use of a small transducer (probe) and ultrasound gel to expose the body to high-frequency sound waves. Ultrasound is safe and painless, and produces pictures of the inside of the body using sound waves. Ultrasound examinations do not use ionizing radiation (as used in x-rays). Because ultrasound images are captured in real-time, they can show the structure and movement of the body's internal organs, as well as blood flowing through blood vessels.
Ultrasound imaging is a noninvasive medical test that helps physicians diagnose and treat medical conditions.
An ultrasound of the thyroid produces pictures of the thyroid gland and the adjacent structures in the neck. The thyroid gland is located in front of the neck just above the collar bones and is shaped like a butterfly, with one lobe on either side of the neck connected by a narrow band of tissue. It is one of nine endocrine glands located throughout the body that make and send hormones into the bloodstream.
The thyroid gland makes the thyroid hormone, which helps to regulate a variety of body functions including how fast the heart beats. It is very common for patchy areas or nodules to develop in the thyroid that may or may not be felt on the skin surface. About five to 10 percent of adults will have lumps in their thyroid that a doctor can identify on an exam. These are called palpable nodules. Ultrasound is very sensitive and shows many nodules that cannot be felt. In some age groups, nodules are seen on ultrasound in as many as 70 percent of adults. The vast majority of these are benign regions of thyroid tissue that pose no health risk. The minorities of these are true tumors of the thyroid and may require further diagnosis or treatment.
What are some common uses of the procedure?
An ultrasound of the thyroid is typically used:
- to determine if a lump in the neck is arising from the thyroid or an adjacent structure
- to analyze the appearance of thyroid nodules and determine if they are the more common benign nodule or if the nodule has features that require a biopsy
- to look for additional nodules in patients with one or more nodules felt on physical exam
- to see if a thyroid nodule has substantially grown over time
Because ultrasound provides real-time images, images that are renewed continuously, it also can be used to guide procedures such as needle biopsies, in which needles are used to extract sample cells from an abnormal area for laboratory testing. Ultrasound may also be used to guide the insertion of a catheter or other drainage device and helps assure accurate placement and fluid drainage for diagnosis or relief of patient discomfort.
How should I prepare?
You should wear comfortable, loose-fitting clothing for your ultrasound exam. You may need to remove all clothing and jewelry in the area to be examined.
You may be asked to wear a gown during the procedure.
No other preparation is required.
Ultrasound examinations are very sensitive to motion, and an active or crying child will slow the examination process. To ensure a smooth experience, it would be beneficial to explain the procedure to the child prior to the exam. You may bring a book to read to the child to ease anxiety. Ultrasound departments often have a television in the examination room and the child's favorite show may be played if there are no other available distractions.
What does the equipment look like?
Ultrasound scanners consist of a console containing a computer and electronics, a video display screen and a transducer that is used to do the scanning. The transducer is a small hand-held device that resembles a microphone, attached to the scanner by a cord. The transducer sends out inaudible high frequency sound waves into the body and then listens for the returning echoes from the tissues in the body. The principles are similar to sonar used by boats and submarines.
The ultrasound image is immediately visible on a video display screen that looks like a computer or television monitor. The image is created based on the amplitude (loudness), frequency (pitch) and time it takes for the ultrasound signal to return from the area of the patient being examined to the transducer, as well as the composition of body tissue through which and the type of body structure the sound travels through.
How does the procedure work?
Ultrasound imaging is based on the same principles involved in the sonar used by bats, ships and fishermen. When a sound wave strikes an object, it bounces back, or echoes. By measuring these echo waves, it is possible to determine how far away the object is and its size, shape and consistency (whether the object is solid or filled with fluid).
In medicine, ultrasound is used to detect changes in appearance of organs, tissues, and vessels or detect abnormal masses, such as tumors.
In an ultrasound examination, a transducer both sends the sound waves and receives the echoing waves. When the transducer is pressed against the skin, it directs small pulses of inaudible, high-frequency sound waves into the body. As the sound waves bounce off of internal organs, fluids and tissues, the sensitive microphone in the transducer records tiny changes in the sound's pitch and direction. These signature waves are instantly measured and displayed by a computer, which in turn creates a real-time picture on the monitor. One or more frames of the moving pictures are typically captured as still images. Small loops of the moving “real time” images may also be saved.
How is the procedure performed?
For most ultrasound exams, the patient is positioned lying face-up on an examination table that can be tilted or moved.
A pillow may be placed behind the shoulders to extend the area to be scanned for a thyroid ultrasound exam. This is especially important for a small child with very little space between the chin and the chest.
A clear water-based gel is applied to the area of the body being studied to help the transducer make secure contact with the body and eliminate air pockets between the transducer and the skin that can block the sound waves from passing into your body. The sonographer (ultrasound technologist) or radiologist then presses the transducer firmly against the skin in various locations, sweeping over the area of interest or angling the sound beam from a farther location to see an area of concern better.
When the examination is complete, the patient may be asked to dress and wait while the ultrasound images are reviewed.
This ultrasound examination is usually completed within 30 minutes.
What will I experience during and after the procedure?
Ultrasound examinations are painless, fast and easily tolerated by most patients.
After you are positioned on the examination table, the radiologist or sonographer will apply some warm water-based gel on your skin and then place the transducer firmly against your body, moving it back and forth over the area of interest until the desired images are captured. There is usually no discomfort from pressure as the transducer is pressed against the area being examined.
If scanning is performed over an area of tenderness, you may feel pressure or minor pain from the transducer.
You may need to extend your neck to help the sonographer (technologist) examine your thyroid with ultrasound. If you suffer from neck pain, inform the technologist so that they can help situate you in a comfortable position for the exam.
Once the imaging is complete, the clear ultrasound gel will be wiped off your skin.
After an ultrasound examination, you should be able to resume your normal activities immediately.
Who interprets the results and how do I get them?
A radiologist, a physician specifically trained to supervise and interpret radiology examinations, will analyze the images and send a signed report to your primary care physician, or to the physician or other healthcare provider who referred you for the exam, who will share the results with you. In some cases the radiologist may discuss results with you at the conclusion of your examination.
Follow-up examinations may be necessary, and your doctor will explain the reason why another exam is needed. Sometimes a follow-up exam is done because a suspicious or questionable finding needs clarification with additional views or a special imaging technique. A follow-up examination may be necessary so that any change in a known abnormality can be monitored over time. Follow-up examinations are sometimes the best way to see if treatment is working or if an abnormality is stable over time.
What are the benefits vs. risks?
Benefits
- Most ultrasound scanning is noninvasive (no needles or
injections).
- Occasionally, an ultrasound exam may be temporarily
uncomfortable, but it is almost never painful.
- Ultrasound is widely available, easy-to-use and less expensive
than other imaging methods.
- Ultrasound imaging is extremely safe and does not use any
ionizing radiation.
- Ultrasound scanning gives a clear picture of soft tissues that do
not show up well on x-ray images.
- Ultrasound provides real-time imaging, making it a good tool for
guiding minimally invasive procedures such as needle biopsies and
needle aspiration.
Risks
- For standard diagnostic ultrasound, there are no known harmful effects on humans.
What are the limitations of an Ultrasound of the Thyroid?
If one or more nodules are detected within the thyroid gland, the radiologist will examine the features of the nodules. Some features are strongly suggestive that a nodule is benign in nature, and some raise concern that the nodule may be a true tumor. In other cases, the radiologist cannot distinguish between benign and malignant lumps with complete certainty. A fine needle biopsy and review of tissue under a microscope may be recommended for further evaluation, but in some cases surveillance and a repeat sonogram after a few months looking for stability may suffice.
It is not possible to determine thyroid function—that is, whether the thyroid gland is underactive, overactive, or normal—with ultrasound. For that determination, your doctor may order a blood test or a radioactive iodine uptake test.