What is an Ultrasound?
For Appointments Call: 786-332-4106 Dade 954-893-3811 Broward
General Ultrasound Imaging
- What is General Ultrasound Imaging?
- What are some common uses of the procedure?
- How should I prepare?
- What does the equipment look like?
- How does the procedure work?
- How is the procedure performed?
- What will I experience during and after the procedure?
- Who interprets the results and how do I get them?
- What are the benefits vs. risks?
- What are the limitations of General Ultrasound Imaging?
What is General Ultrasound Imaging?
Ultrasound imaging, also called ultrasound scanning or sonography, involves the use of a small transducer (probe) and ultrasound gel to expose the body to high-frequency sound waves. Ultrasound is safe and painless, and produces pictures of the inside of the body using sound waves. Ultrasound examinations do not use ionizing radiation (as used in x-rays). Because ultrasound images are captured in real-time, they can show the structure and movement of the body's internal organs, as well as blood flowing through blood vessels.
Ultrasound imaging is a noninvasive medical test that helps physicians diagnose and treat medical conditions.
Conventional ultrasound displays the images in thin, flat sections of the body. Advancements in ultrasound technology include three-dimensional (3-D) ultrasound that formats the sound wave data into 3-D images. Four-dimensional (4-D) ultrasound is 3-D ultrasound in motion.
A Doppler ultrasound study may be part of an ultrasound examination.
Doppler ultrasound is a special ultrasound technique that evaluates blood flow through a blood vessel, including the body's major arteries and veins in the abdomen, arms, legs and neck.
There are three types of Doppler ultrasound:
- Color Doppler uses a computer to convert Doppler measurements into an array of colors to visualize the speed and direction of blood flow through a blood vessel.
- Power Doppler is a newer technique that is more sensitive than color Doppler and capable of providing greater detail of blood flow, especially when blood flow is little or minimal. Power Doppler, however, does not help the radiologist determine the direction of blood flow, which may be important in some situations.
- Instead of displaying Doppler measurements visually, Spectral Doppler displays blood flow measurements graphically, in terms of the distance traveled per unit of time.
What are some common uses of the procedure?
Ultrasound examinations can help to diagnose a variety of conditions and to assess organ damage following illness.
Ultrasound is used to help physicians evaluate symptoms such as:
- pain
- swelling
- infection
- hematuria (blood in urine)
Ultrasound is a useful way of examining many of the body's internal organs, including but not limited to the:
- heart and blood vessels, including the abdominal aorta and its major branches
- liver
- gallbladder
- spleen
- pancreas
- kidneys
- bladder
- uterus, ovaries, and unborn child (fetus) in pregnant patients
- eyes
- thyroid and parathyroid glands
- scrotum (testicles)
- brain in infants
- hips in infants
Ultrasound is also used to:
- guide procedures such as needle biopsies, in which needles are used to extract sample cells from an abnormal area for laboratory testing.
- image the breasts and to guide biopsy of breast cancer (see the Ultrasound-Guided Breast Biopsy page (www.RadiologyInfo.org/en/info.cfm?pg=breastbius)).
- diagnose a variety of heart conditions and to assess damage after a heart attack or diagnose for valvular heart disease.
Doppler ultrasound images can help the physician to see and evaluate:
- blockages to blood flow (such as clots).
- narrowing of vessels.
- tumors and congenital vascular malformation.
With knowledge about the speed and volume of blood flow gained from a Doppler ultrasound image, the physician can often determine whether a patient is a good candidate for a procedure like angioplasty.
How should I prepare?
You should wear comfortable, loose-fitting clothing for your ultrasound exam. You may need to remove all clothing and jewelry in the area to be examined.
You may be asked to wear a gown during the procedure.
Other preparation depends on the type of examination you will have. For some scans your doctor may instruct you not to eat or drink for as many as 12 hours before your appointment. For others you may be asked to drink up to six glasses of water two hours prior to your exam and avoid urinating so that your bladder is full when the scan begins.
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
What does the equipment look like?
Ultrasound scanners consist of a console containing a computer and electronics, a video display screen and a transducer that is used to do the scanning. The transducer is a small hand-held device that resembles a microphone, attached to the scanner by a cord. The transducer sends out inaudible high frequency sound waves into the body and then listens for the returning echoes from the tissues in the body. The principles are similar to sonar used by boats and submarines.
The ultrasound image is immediately visible on a video display screen that looks like a computer or television monitor. The image is created based on the amplitude (loudness), frequency (pitch) and time it takes for the ultrasound signal to return from the area of the patient being examined to the transducer, as well as the composition of body tissue through which and the type of body structure the sound travels through.
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
How does the procedure work?
Ultrasound imaging is based on the same principles involved in the sonar used by bats, ships and fishermen. When a sound wave strikes an object, it bounces back, or echoes. By measuring these echo waves, it is possible to determine how far away the object is and its size, shape and consistency (whether the object is solid or filled with fluid).
In medicine, ultrasound is used to detect changes in appearance of organs, tissues, and vessels or detect abnormal masses, such as tumors.
In an ultrasound examination, a transducer both sends the sound waves and receives the echoing waves. When the transducer is pressed against the skin, it directs small pulses of inaudible, high-frequency sound waves into the body. As the sound waves bounce off of internal organs, fluids and tissues, the sensitive microphone in the transducer records tiny changes in the sound's pitch and direction. These signature waves are instantly measured and displayed by a computer, which in turn creates a real-time picture on the monitor. One or more frames of the moving pictures are typically captured as still images. Small loops of the moving “real time” images may also be saved.
Doppler ultrasound, a special application of ultrasound, measures the direction and speed of blood cells as they move through vessels. The movement of blood cells causes a change in pitch of the reflected sound waves (called the Doppler effect). A computer collects and processes the sounds and creates graphs or color pictures that represent the flow of blood through the blood vessels.
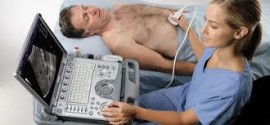
How is the procedure performed?
For most ultrasound exams, the patient is positioned lying face-up on an examination table that can be tilted or moved.
A clear water-based gel is applied to the area of the body being studied to help the transducer make secure contact with the body and eliminate air pockets between the transducer and the skin that can block the sound waves from passing into your body. The sonographer (ultrasound technologist) or radiologist then presses the transducer firmly against the skin in various locations, sweeping over the area of interest or angling the sound beam from a farther location to see an area of concern better.
Doppler sonography is performed using the same transducer.
When the examination is complete, the patient may be asked to dress and wait while the ultrasound images are reviewed.
In some ultrasound studies, the transducer is attached to a probe and inserted into a natural opening in the body. These exams include:
- Transesophageal echocardiogram. The transducer is inserted into the esophagus to obtain images of the heart.
- Transrectal ultrasound. The transducer is inserted into a man's rectum to view the prostate.
- Transvaginal ultrasound. The transducer is inserted into a woman's vagina to view the uterus and ovaries.
Most ultrasound examinations are completed within 30 minutes to an hour.
What will I experience during and after the procedure?
Ultrasound examinations are painless, fast and easily tolerated by most patients.
After you are positioned on the examination table, the radiologist or sonographer will apply some warm water-based gel on your skin and then place the transducer firmly against your body, moving it back and forth over the area of interest until the desired images are captured. There is usually no discomfort from pressure as the transducer is pressed against the area being examined.
If scanning is performed over an area of tenderness, you may feel pressure or minor pain from the transducer.
Ultrasound exams in which the transducer is inserted into an opening of the body may produce minimal discomfort.
If a Doppler ultrasound study is performed, you may actually hear pulse-like sounds that change in pitch as the blood flow is monitored and measured.
Once the imaging is complete, the clear ultrasound gel will be wiped off your skin.
After an ultrasound examination, you should be able to resume your normal activities immediately.
Who interprets the results and how do I get them?
A radiologist, a physician specifically trained to supervise and interpret radiology examinations, will analyze the images and send a signed report to your primary care physician, or to the physician or other healthcare provider who referred you for the exam, who will share the results with you. In some cases the radiologist may discuss results with you at the conclusion of your examination.
Follow-up examinations may be necessary, and your doctor will explain the reason why another exam is needed. Sometimes a follow-up exam is done because a suspicious or questionable finding needs clarification with additional views or a special imaging technique. A follow-up examination may be necessary so that any change in a known abnormality can be monitored over time. Follow-up examinations are sometimes the best way to see if treatment is working or if an abnormality is stable over time.
What are the benefits vs. risks?
Benefits
- Most ultrasound scanning is noninvasive (no needles or injections).
- Occasionally, an ultrasound exam may be temporarily uncomfortable, but it is almost never painful.
- Ultrasound is widely available, easy-to-use and less expensive than other imaging methods.
- Ultrasound imaging is extremely safe and does not use any ionizing radiation.
- Ultrasound scanning gives a clear picture of soft tissues that do not show up well on x-ray images.
- Ultrasound is the preferred imaging modality for the diagnosis and monitoring of pregnant women and their unborn babies.
- Ultrasound provides real-time imaging, making it a good tool for guiding minimally invasive procedures such as needle biopsies and needle aspiration.
Risks
- For standard diagnostic ultrasound, there are no known harmful effects on humans.
What are the limitations of General Ultrasound Imaging?
Ultrasound waves are disrupted by air or gas; therefore ultrasound is not an ideal imaging technique for air-filled bowel or organs obscured by the bowel. In most cases, barium exams, CT scanning, and MRI are the methods of choice in this setting.
Large patients are more difficult to image by ultrasound because greater amounts of tissue attenuates (weakens) the sound waves as they pass deeper into the body.
Ultrasound has difficulty penetrating bone and, therefore, can only see the outer surface of bony structures and not what lies within (except in infants who have more cartilage in their skeletons than older children or adults). For visualizing internal structure of bones or certain joints, other imaging modalities such as MRI are typically used.